
Many females connect their monthly cycles with vaginal bleeding. However, it is not unusual to bleed between periods, and you can see several explanations for spotting between phases. Although some light spots may be benign, sometimes bleeding between stages may signal a health problem or pregnancy.
What does it mean if I experience bleeding during ovulation?
Ovulation bleeding usually relates to bleeding, which happens when the ovary produces an egg. Estrogen concentrations continuously increase in the days leading to ovulation after releasing an egg, the levels of estrogen decrease, and the masses of progesterone rise.
This change in the equilibrium between estrogen and progesterone concentrations can trigger light bleeding, which is often much slower than standard bleeding times. In most instances, no other signs occur.
If an individual has other signs, such as cramping, next to the wound, or lasting longer than a few days, the fundamental cause may be something other than an ovulation injury.
People who don’t ovulate frequently may have extraordinary bleeding habits, such as very light bleeding for many days, or just a few months. Many medical circumstances, such as PCOS and endometriosis, can lead to irregular cycles.
When does ovulation spotting happen?
Ovulation usually takes place everywhere between 11 and 21 days following the first day of your last period. Although in some women, depending on the length of your cycle, it may happen sooner or later. Ovulation may also occur at distinct moments during a woman’s period and may take place each month on a separate day.
Ovulation tracking can assist enhance your likelihood of getting pregnant. Ovulation is also tracked by some females to avoid pregnancy. If you try to get married, light painting may be an indication that you can think about your cycle around this moment.
Read also: Early signs pregnancy
Note that an egg is only accessible for fertilization during ovulation for about 12-24 hours. Your reproductive chance is about five days each month because sperm can reside in your body for three to five days.
It implies you can still get pregnant if you have unprotected sex four days before you ovulate. However, it is doubtful that you will become pregnant if you have sex the day after ovulation unless you have a very brief period.
How do I identify it?

If you realize that it spots around the center of your cycle, it can distinguish ovulation. The figure is light vaginal bleeding outside of your periodic intervals. This bleeding is typically much slower than what you’re going to encounter if you have your time.
The color of the blood can be indicative of the cause. It is because of the color shifts according to the blood flow speed. Some females define detecting ovulation as pink or red.
Pink spotting is an indication of the mixture of blood and cervical fluid. Women generate more cervical fluid when ovulation occurs. The detection of ovulation generally takes one or two days.
Why do I experience spotting?
For many purposes, intermenstrual bleeding may happen. While some are ordinary, others show that you should talk to your doctor about a health situation. Cysts, pregnancy, or perimenopause ordinarily point to period spotting.
- Pre-menarche bleeding happens for the first moment before a teenage woman menstruates. In general, this is benign.
- PCOS is a frequent fertility disease where several tiny cysts develop on one or both of the ovaries. Polycystic ovarian syndrome. Hormonal imbalance and anovulation can lead to mid-cycle spotting or the absence of ovulation.
Read also: A closer look at new choice pregnancy test kit
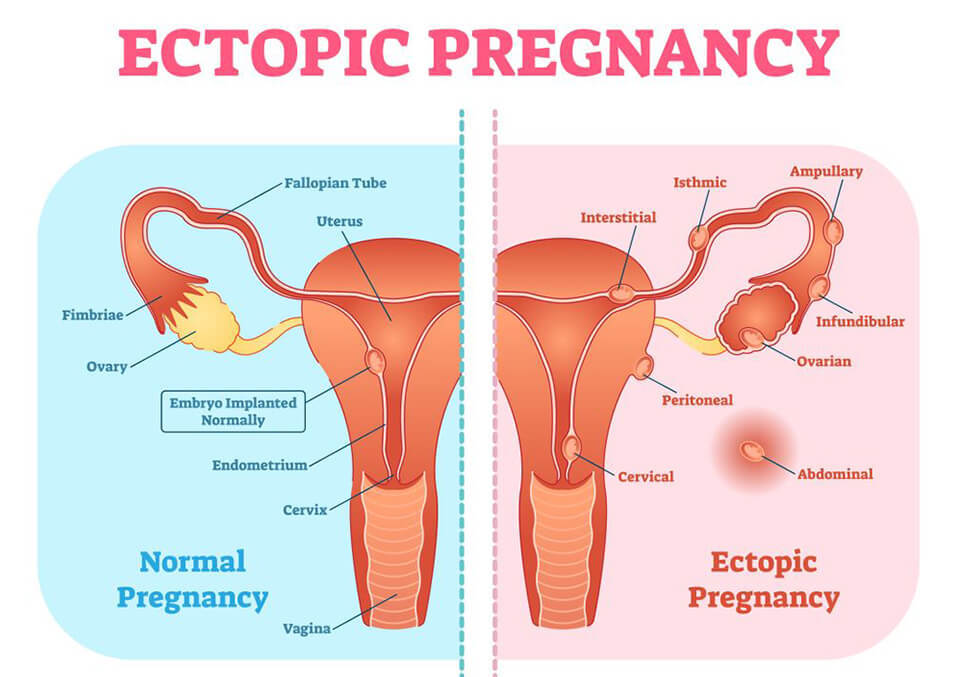
- Ectopic pregnancy is a kind of gestation that implants the fertilized egg and develops outside the uterus. One speculation for intermenstrual vaginal infection may be an ectopic gestation. Ectopic pregnancies can cause severe health problems.
Other occasions, period spotting, may show an infection, sexually transmitted or otherwise. Some STDs can cause bleeding, including chlamydia, pelvic inflammatory disease, or HPV.
If you understand that you have unprotected sex, contact your primary health care professional if you encounter spots. Sexually borne diseases can lead, when remaining untreated, to severe sexual problems, including infertility.
Can I become pregnant while spotting?

Some non-menstrual bleeding can show that it is pregnant or complicated. However, you may become pregnant if you see implantation bleeding (and it can be hard to determine) between stages. For instance, young girls who haven’t had their first menstrual period can pregnant in advance.
Mid-cycle bleeding is an indication of fertility, but many physicians think that it is not an indication of your pregnancy. Brown mid-cycle spotting may show the best time to attempt and conceive.
You can use over-the-counter ovulation screening kits if you try to become pregnant. However, if you have some threat variables like STDs, and you might be pregnant or are trying to have one, you can have a vulnerability to sexual cancer or nearing menopause. Revisit your ob-gyn to distinguish the origin of your menstrual bleeding.
Read also: All you need to know about 3d 4d scanning
Your doctor will ask you several inquiries concerning the spotting of your ovulation. The more data you can contribute; the more accurate your diagnosis will be. Some treatment preferences may involve lifestyle adjustments such as weight loss, dietary supplements, or hormonal birth controls or supplements.
Other medications, such as childbirth or cancer therapy, may be particular to the root cause of your disease. Intermenstrual bleeding has many reasons, from benign to severe, so that adequate diagnosis and treatment are essential to your health.
Fact:
Though researchers begin to examine the spotting of ovulation, they don’t understand precisely why or if it is an indication of something with a healthcare supplier. But there is no proof at present that ovulation spotting is a source for worry.
Irregular bleeding and incompatible detection can predict other fundamental health problems. Talk to your healthcare supplier if you bleed between periods frequently or encounter uncommon severe bleeding between periods.
Takeaway
Blooding between time intervals is prevalent and affects 9–14% of women between menarche and menopause. Although ovulation bleeding is a frequent source of pregnancy between stages, it is not the only possible source. It is therefore essential to monitor the bleeding and discuss any troubling signs with your doctor.
As the menstrual cycle can be different for everyone, a person might want to track their cycle to determine the regular cycle length and the typical ovulation day. This information can often assist a doctor in deciding whether ovulation or anything else causes bleeding.
Read also:
- Everything You Need to Know About Ovulation
- The Ovulation And Vaginal Discharge During Pregnancy
- Ovulation Facts Revealed: Everything You Need To Know


