
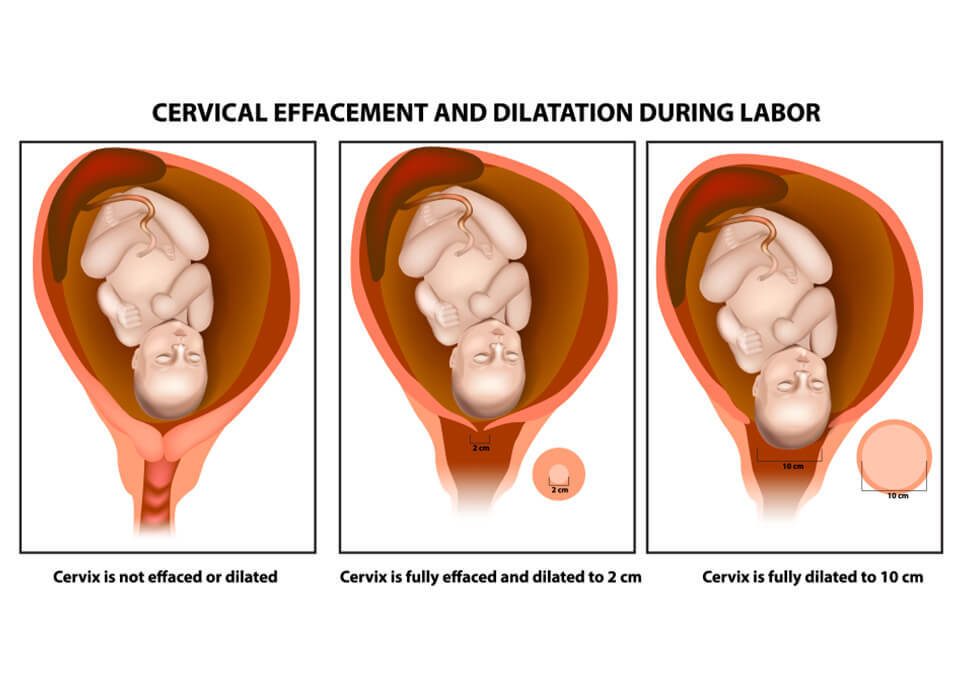
When a female has a child, a cervical dilation cycle exposes the cervix, which is the lower part of the vagina. The sequence of the opening of the cervix is one way that health workers monitor the success of the delivery of a person. At operation, the cervix extends to the uterus, which is roughly 10 cm (3) “for most term infants, to support the baby’s head.
For example, if the cervix is not closed, a person is not in labor. But if her cervix opens regularly, she becomes healthy and closer to delivering her child. Usually, the cervix dilates gradually as a woman develops through the periods of delivery.
What does it mean when you dilate during pregnancy?
It doesn’t necessarily mean that it just takes hours or days to dilate to 1 centimeter. The cervix can be dilated for weeks until delivery begins to 1 centimeter. The level of dilation also indicates that the cervix is beginning to operate.
The cervix is a slight passage connecting the uterus and the vagina. Through active labor, the cervix dilates up to 10 cm. The cervix will already undergo many modifications by this time.
The cervical opening enables the lining of the vagina to escape through menstruation. Hormones thicken the mucus in the cervix during gestation, complete the opening, and create the so-called mucus barrier in the medical community to shield the fetus.
For most of the delivery, this plug is in place. In the third trimester, though, the cervix starts to decline and contract, in a process called discharge.
The width of the cervix also starts to extend and expand. A health care provider typically determines the degree of dilation or erasure during routine visits. It is not surprising for a doctor to acknowledge 1 cm of dilation as a pre-delivery indication.
Labor and dilation

The time between growth and conception varies between women and babies. One female can be born in several hours from having a closed cervix, whereas another is 1-2 cm dilated for days and weeks.
Many women will not be dilated until they go to active labor. It ensures the cervix is formerly wholly closed, but as the study continues, it is expanded to 10 cm. In early pregnancy, it is particularly common. For other ladies, particularly those who experienced delivery before, dilation may commence a few days or weeks before labor starts.
Dilation alone is not seen as a labor mark but as a way of preparing the body for labor. Someone involved in early dilation should speak to the nurse. The doctor shall determine the level of enlargement and any other signs of imminent arrival.
What do you need to know about effacement and dilation?
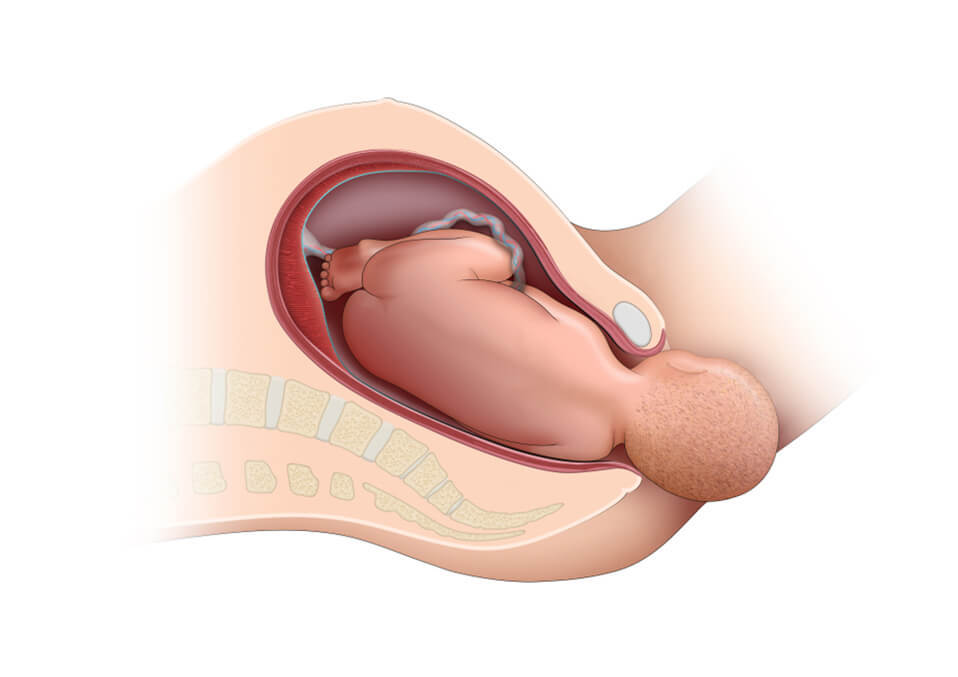
Beginning in your ninth month of gestation, the doctor will look for confirmation of advancement closer together, active belly, and an internal investigation to examine your cervix. In addition to seeing if the child has fallen, you check if the cervix has widened or removed if it has started to weaken or transfer to the pelvic front.
Based on these factors, she would probably guess what you arrive. But don’t drive to the hospital right now if the estimate is “soon.” There are a hundred women who are still pregnant and anxious for each doctor who gets the money a week ago.
The “cork” of mucosa that covers the opening of the cervix dislodges as it begins to shrink and expand. You may or may not notice this, and it may occur everywhere between a few weeks and hours before labor begins. Then you will find bleeding displays a few days to 24 hours before birth.
Read also: “Labor: Odd and Weird Signs”
Capillaries in your cervix start to burst, stain vaginal mucus red, and smear it with blood. As job contractions are slowly increased and even when you change positions, you’re going to know that the time is eventually close!
Your cervix will continue to delete and dilate throughout this cycle. During early labor, the cervix dilates to about 3 centimeters; this rises to about 7 cm by active labor. After the transitional phase, the full cervical dilation happens when the cervix reaches 10 cm. It’s time to start moving the child out once this happens.
What are the indications of labor?
These are some common signs that labor has started or will start soon.
- The contractions
Less common signs are that labor has started or will soon begin.
Tightening and relaxing of the uterine muscle are contractions. Most females experience contractions during childbirth. These are normal, although they can be worried if a person is first pregnant. When contractions occur before labor, the medicinal population calls them contractions of Braxton-Hicks.
They are the body’s way of healing the muscles that deliver the baby. The critical variations in length, severity, and associated pain between Braxton-Hicks and labor contractions. When contractions are spontaneous or painless, Braxton-Hicks contractions are likely.
Read also: “everything you need to know about ovulation”
Contracts transpiring near a due date are ordinarily more frequent, longer-term, and uncomfortable. The interval between contractions is an indispensable indicator of delivery. Let a healthcare provider know when contractions occur regularly and cause pain.
- Losing the bubble with mucus
When pregnancy begins, the opening of the cervix is closed with a mucus plug. This plug breaks down and reduces as dilation continues. If the cap comes out, it might appear like a discharge. The hue will vary from white to purple, and the connection is somewhat blurred. In a few days or weeks after losing the mucus plug, a person may go to labor.
- Water breaking
When labor begins, the baby’s membrane will break up and fall apart. The dissolution of water is one of the most common signs of operation. It can cause a sudden fluid gush or just a trick. Some women may not notice that it’s so fluid. Notify the physician of any water loss and other signs such as pressures and contractions.
Final words
After the daunting process of going through the stages of pregnancy is done, the body of a woman takes time to return to her unpregnant condition. It takes approximately six weeks on average for the vagina to return to its non-small size and for the cervix to close.
Read also:
- What to Expect on the Last Two Weeks of Pregnancy
- Natural Ways On How To Speed Up Labor During Pregnancy
- Phantom Pregnancy, False Pregnancy or Pseudocyesis Guide?


