Spina bifida is a birth condition wherein the spin and the spinal cord of the baby didn’t form properly. There is an imperfect closing of the spine and membranes around the spinal cord through the development of the early stages of pregnancy. The neural pipe is the embryonic assembly that ultimately progresses into the infant’s brain and spinal cord and the tissues that enfold them.
Under normal circumstances, the neural tube forms during the early stages of pregnancy, and it eventually closes by the twenty-eighth day after conception. In infants with the defect of Spina bifida, part of the neural tube fails to progress or enclosed properly, leading or causing defects in the bones of the spine and spinal cord.
This defect can be diagnosed from mild to severe depending on the case, type of Spina bifida type, size, place, and problems.
Spina bifida types
Spina bifida is often diagnosed depending on what type of Spina bifida the infant has. This ailment consists of different types and severity. Spina occurs in different forms. So, it is in the best interest to have your child tested to confirm what Spina bifida they have.
1. Spina bifida occulta

One of the mildest forms of this defect is the Occulta which means “hidden”. It only means that most people who have this type of defect don’t usually know they have this type of illness. This type of defect isn’t usually detected by normal testing. The condition is often discovered by an imaging test
2. Meningocele
Meningocele is also the type of Spina bifida that affects babies. The protective membranes around the spinal cord are pushed out of the opening in the vertebrae causing to form a sac-filled with liquids. But the sac isn’t involved in the spinal cord, so the chances of having nerve damages are slim, although there are later problems that ensue during the later parts of complications.
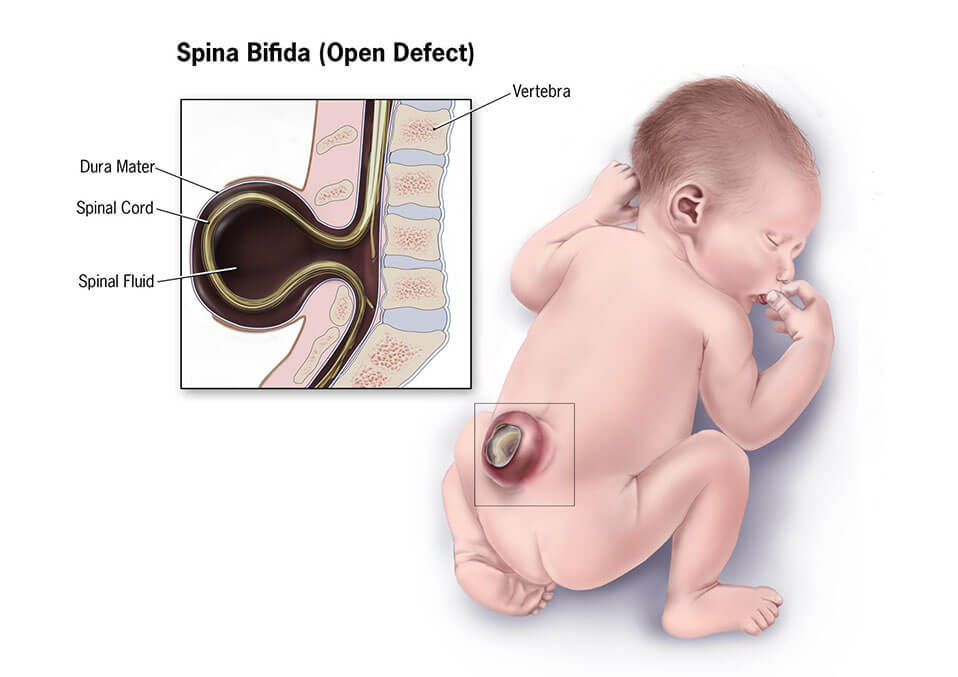
3. Myelomeningocele
One of the most serious and lethal forms of Spina Bifida as it causes babies to have life-threatening infections. The spinal waterway is exposed along numerous vertebrae in the lower or central back. The spinal nerves and membranes are pushed through the opening much like the Meningocele. Unlike the meningocele, the sac is formed at the baby’s back revealing tissues and nerves.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms are varied depending on the type of Spina bifida the patient has. It can also differ from person to person.
- Spina bifida – Because nerves on the spine aren’t usually involved, there are typically no signs and symptoms. But in rare cases, there are some visible indications which tell that the baby has cases that can be seen outside, it can be usually seen at the newborn’s skin above the spinal defect which includes a tuft of hair or a little dimple.
- Meningocele – While it doesn’t include the spinal cord, there are membranes that are pushed out through the opening that forms sac-filled fluids.
- Myelomeningocele– Along the lower or middle back of several vertebrae, the spinal ways are open. And during birth, the membranes and spinal are protruded at the baby’s back thus forming a sac. And although skin covers the sac in some cases, tissues and nerves are usually exposed.
What causes spina bifida?
Licensed physicians still aren’t sure what causes spina-bifida. As with many other conditions or problems, it seems to be the end result of a combination of environmental risk factors and genetics.
Treatments

People that are born with Spina Bifida have different needs; it is not the same with any other patients. Some people have different Spina bifida, and other types of Spina bifida are treated differently. So, it is best to know what type of Spina bifida the baby has. Babies with Meningocele and Myelomeningocele are more treated with more treatments because these are the types of Spina bifida that are severe and cause life-threatening infections.
Risk factors
Although some licensed physicians and researchers still don’t know what the causes of Spina bifida and these are identified to have risk factors.
- Folate deficiency- Folate is one of the most important baby needs for its development. A deficiency in folate may add to the risks of having your baby a Spina bifida or other neural tube defects.
- Medications- Some medications such as Valproic may seem to cause some neural tube damage if taken during pregnancy, because these types of drugs may have the tendency to affect the baby’s ability to use folate and folic acid.
- Diabetes- Pregnant women who have diabetes are at a higher risk of having a baby with Spina bifida because of their ability to can’t control their blood sugar,
- Obesity- Pre-pregnancy is often associated with higher risks of having neural tube defects, and this includes spina bifida.
- Higher body temperature- Some studies have shown that having higher body temperatures during the early stages of pregnancy may increase the effect of having your newborn with Spina bifida. Upping your body temperature has been associated with the possible risk of Spina Bifida.
- Family history/Genetics- A woman who was born with neural tube defects can pose a greater risk of having their child get Spina bifida. However, infants who are born with Spina bifida aren’t known to have their parents have Spina bifida
Complications
Spina bifida may cause a little or minimal physical disability to your newborn. But in most severe cases, it can cause significant at permanent disability to your child. The severity is often associated with the type of Spina bifida your child has.
There is also a list of complications that Spina bifida can possibly give to your child. And parents may be overwhelmed at this, but remember that not all children can have these. And these complications have treatments.
- Walking and Mobility problems- With children that are born with Spina bifida, it usually affects their leg movement and they don’t work properly. The nerves that control their leg movements are restricted causing muscle weakness and sometimes it involves paralysis. So, the moment your kids have Spina bifida, it is your #1 concern to care for them.
- Skin Problems- Kids with Spina bifida may have wounds in their legs, feet or back. And most of the time, they can’t feel this, in result forming blisters and sores that can turn into wounds or infections that are hard to treat.
- Other complications- Many complications may still arise with children having Spina bifida as they age. Such as disorders in the urinary tract and gastrointestinal tract.
Prevention
It is important to take Folic acid supplements during the first-month pregnancy after conception as it helps the risk of having your newborn Spina bifida. It greatly reduces the risk
Conclusion
Spina bifida is an ailment that you should be worried about. It is always important to have your weekly visit to your doctor. It is also the best way to prevent this type of disease to perform tests to avoid Spina bifida or to minimize its damage during its early stages. The health of your child will be your concern moving forward. So, it is best to keep an eye on everything your pregnant wife does or eats. It is always the prevention that is better than a cure. Be vigilant and never take anything for granted.
Read also:
- Guidelines on Bone Health for Kids
- The Ultrasound at 20 Weeks of Pregnancy
- Vaccines: Does my Kid Need to Take the Shot?


