Pregnancy is a miraculous and exciting journey, but unfortunately, not all pregnancies end in a healthy baby.
Miscarriage, stillbirth, and ectopic pregnancy are heartbreaking experiences that affect many women around the world.
While it is difficult to talk about, recognizing the signs of non-viable pregnancy is crucial for early detection and proper medical intervention.
As a woman, understanding what to look out for and when to seek medical attention can make a significant impact on your health and future fertility.
In this article, we will delve into the signs and symptoms of a non-viable pregnancy, the different types of pregnancy loss, and what to expect during and after a miscarriage or stillbirth.
By educating ourselves and others, we can break the silence surrounding pregnancy loss and support those who have experienced it.
Understanding non-viable pregnancy
A non-viable pregnancy, also known as a failed pregnancy, is a pregnancy that has stopped developing.
The fetus may have stopped growing or may have not developed correctly, leading to an inability to sustain a live pregnancy. Non-viable pregnancies include miscarriage, stillbirth, and ectopic pregnancy.
Miscarriage is the most common type of non-viable pregnancy, occurring in 10-20% of all pregnancies. It is defined as the loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week of gestation.
Stillbirth, on the other hand, occurs after the 20th week of gestation, and the baby is born without signs of life. Ectopic pregnancy is when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube, and is not viable.
Signs and symptoms of non-viable pregnancy
The signs and symptoms of a non-viable pregnancy can vary depending on the type of pregnancy loss. In the case of miscarriage, the most common symptoms are vaginal bleeding, cramping, and the passing of tissue or clots.
However, some women may not experience any symptoms and may only find out during a routine ultrasound.
Stillbirth may have no symptoms, or the mother may notice a decrease in fetal movement or no movement at all.
Ectopic pregnancy can cause sharp abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and shoulder pain. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Causes of non-viable pregnancy
Non-viable pregnancies can be caused by a variety of factors, including chromosomal abnormalities, maternal health conditions, and lifestyle factors.
Chromosomal abnormalities are the most common cause of miscarriage, where the fetus has an extra or missing chromosome.
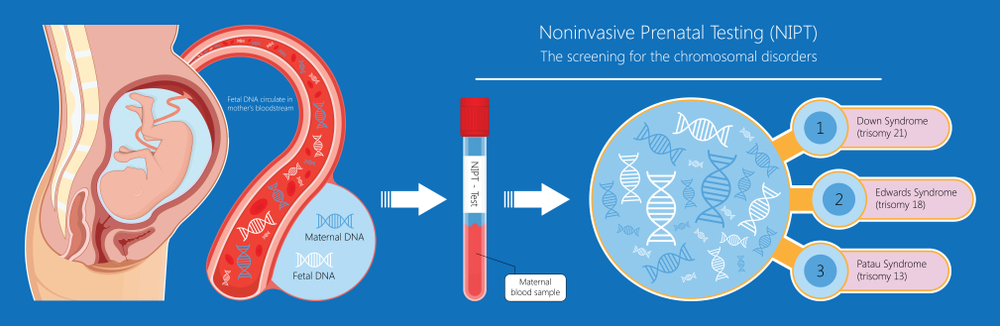
Maternal health conditions, such as thyroid disease or diabetes, can also increase the risk of non-viable pregnancy.
Lifestyle factors, such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use, can also increase the risk of non-viable pregnancy.
In the case of ectopic pregnancy, a history of pelvic inflammatory disease or previous ectopic pregnancy can increase the risk.
How non-viable pregnancy is diagnosed
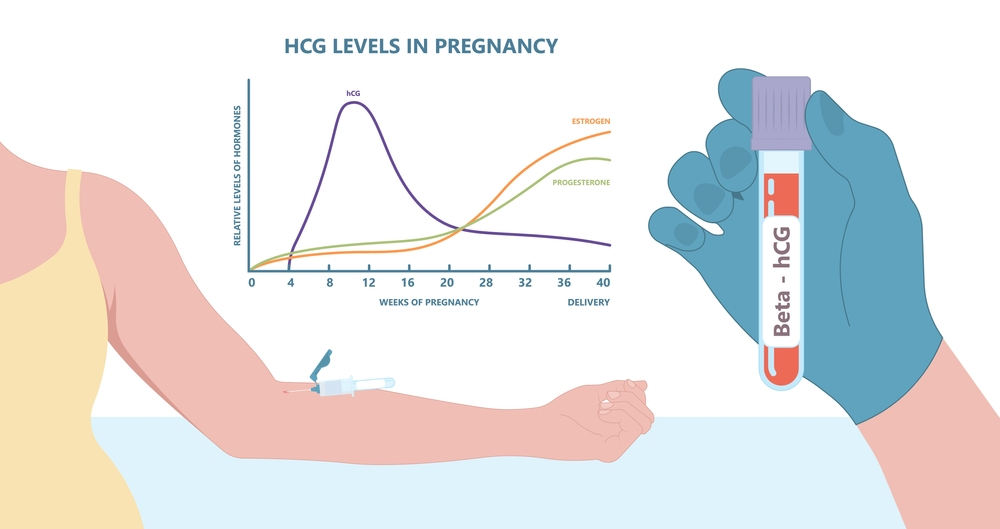
Non-viable pregnancy is typically diagnosed through an ultrasound scan. The scan can detect if the fetus has stopped growing or if there is no heartbeat.
Blood tests may also be done to check hormone levels, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which can indicate if the pregnancy is viable.
In the case of ectopic pregnancy, a transvaginal ultrasound may be done, or laparoscopic surgery may be required to remove the fertilized egg.
Treatment options for non-viable pregnancy
The treatment options for non-viable pregnancy depend on the type of pregnancy loss and the stage of pregnancy.
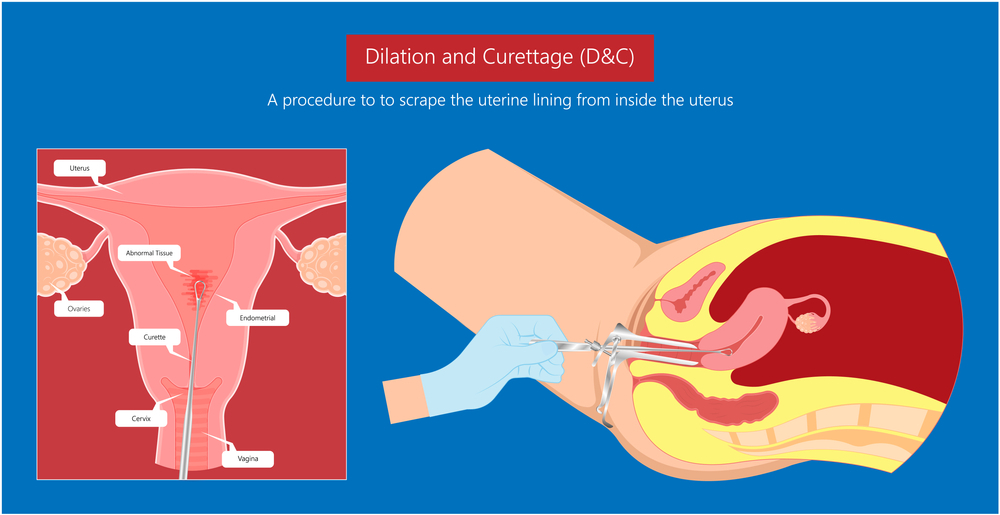
In the case of miscarriage or stillbirth, the options may include expectant management, medication to induce labor, or surgical intervention. Expectant management involves waiting for the body to expel the fetal tissue naturally.
Medication to induce labor may be used to speed up the process, and surgical intervention, such as dilation and curettage (D&C), may be required if the fetal tissue does not pass naturally.
In the case of ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg must be removed promptly to prevent further complications, such as rupture and internal bleeding. Treatment options may include medication to dissolve the fertilized egg or surgery to remove the affected fallopian tube.
Coping with the emotional impact of non-viable pregnancy
The emotional impact of non-viable pregnancy can be overwhelming and challenging to navigate.
It is essential to seek support from loved ones, healthcare professionals, or support groups. Many women experience a range of emotions, including sadness, guilt, anger, and anxiety.
It is essential to allow yourself to grieve and process your emotions in your own time. Counseling or therapy may also be helpful in coping with the emotional impact of non-viable pregnancy.
What to expect during and after a non-viable pregnancy
The physical recovery after a non-viable pregnancy can vary depending on the type of pregnancy loss and the treatment option chosen.
In the case of miscarriage or stillbirth, it is normal to experience bleeding and cramping for several days to weeks after the loss.
It is essential to follow up with your healthcare provider to ensure that the pregnancy loss is complete, and there are no further complications.
In the case of ectopic pregnancy, it may take several weeks to recover from surgery or medication.
When to try again after non-viable pregnancy
The decision to try again after a non-viable pregnancy can be challenging and personal. It is essential to discuss with your healthcare provider when it is safe to try again, as this can vary depending on the type of pregnancy loss and the treatment received.
In general, it is recommended to wait until after one menstrual cycle to allow the body to heal physically and emotionally.
It is crucial to take the time to process your emotions and seek support before trying again.

Preventing non-viable pregnancy in the future
Preventing non-viable pregnancy can be challenging, as many factors can contribute to pregnancy loss.
However, taking care of your health before and during pregnancy can reduce the risk of non-viable pregnancy.
It is essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding harmful substances such as tobacco, alcohol, and drugs.

Seeking proper prenatal care and monitoring any pre-existing health conditions can also reduce the risk of pregnancy loss.
Non-viable pregnancy is a challenging and heartbreaking experience that affects many women around the world.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a non-viable pregnancy and seeking medical attention early can make a significant impact on your health and future fertility.
It is crucial to seek support from loved ones, healthcare professionals, or support groups to cope with the emotional impact of non-viable pregnancy. Remember to take the time to grieve and process your emotions in your own time.
By educating ourselves and others and breaking the silence surrounding pregnancy loss, we can support those who have experienced it and raise awareness of the importance of early detection and proper medical intervention.


