
My kids are healthy, do they need to take the vaccines? Why are there so many shots that are required for my kids? Is it okay to skip some of it? My kid has allergies, will the vaccine be able to put him in more danger? Will it cause any other diseases and harmful side effects?
These are some of the questions that parents often asked when the topic of vaccination comes up. Misinformation may cause scare among parents that they sometimes decide to skip or stop immunizing their children. If only they know it doing it will only put their kids’ life in greater risks of illnesses and worst, even death. Immunization is vital in keeping kids healthy and protected against other diseases.
Read also: What are some psycho behaviors in kids
Although babies have antibodies that are passed to them by their mothers even before birth and breastfeeding gives them more antibodies, these are just temporal. They need to be protected always.
What is vaccination and how is it done?
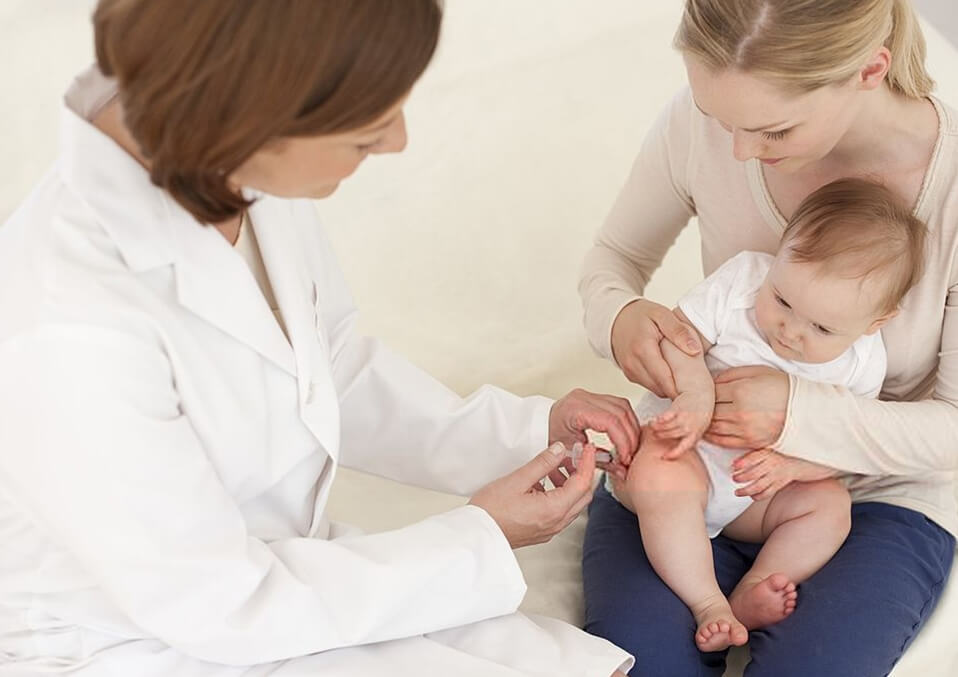
Immunization or vaccination is a way to give immunity or protection to the body against disease. It will prepare the body to fight illnesses. It is done by using a part of a dead or weakened germ that causes the disease. Germs can either by viruses or bacteria that carry the disease. The body will practice fighting the disease by making antibodies that recognize the germ. If the body will then be exposed to the germ of the actual disease, the antibodies are already set up and the body is prepared to fight it and the body will not get sick.
Illnesses that can be prevented by vaccination
Measles
This is a highly contagious airborne viral infection. Someone who has it who coughs or sneeze can pass on the virus to another. There is a 90% possibility that someone who gets near to a person who has it can be infected once the carrier sneezes or coughs near him. It attacks the respiratory system, like the lungs and bronchial tubes. It can cause pneumonia, brain swelling, and death. When anti-measles vaccines are not yet available, millions in the US contracted the disease each year which killed almost 500.
Flu
Flu is another viral infection of the nose, throat, and lungs. Those who came in contact with a person infected by the virus up to 6 feet away can get infected. It can be passed through the air and by touching. It will lead to other serious complications for those with asthma and diabetes.
Polio
This is a viral disease that affects the muscle, causing a person to be crippled for life. One can get infected by contact with a sick person’s feces. It has flu-like symptoms but can later cause brain infection, paralysis, and death.
Pneumococcal Disease
This a bacterial disease that causes pneumonia, meningitis (which affects the brain and the spinal cord), ear and blood infections. It is easily transferred through a sick person’s mucus or saliva. This can lead to complications that can be fatal.
Tetanus
A bacterial disease that causes lockjaw, muscle spasm, paralysis, breathing problems, and death. Bacteria that cause the disease are found in the soil, dust, and feces. It can enter the body through cuts and open wounds. Twenty percent of tetanus cases can be fatal.
Read also: What are the top educational apps for kids
These are just a few illnesses that can be prevented with proper care, sanitation and of course, immunization. There are a lot more like Hepatitis B, Diptheria, rabies, chickenpox, mumps, pertussis and meningococcal infections among others. But cases of these dangerous childhood illnesses decrease dramatically because of vaccination.
It is also a false notion that immunization weakens the immune system. Our body produces antibodies to protect itself. Others are scared since because vaccines inject the germ to the kid’s body. Worry not. Babies’ immune system is far stronger than what they receive in a vaccine. Besides, it contains s just a part of that dead germ which is usually just a small percent of what babies’ immune system can handle.
Side effects
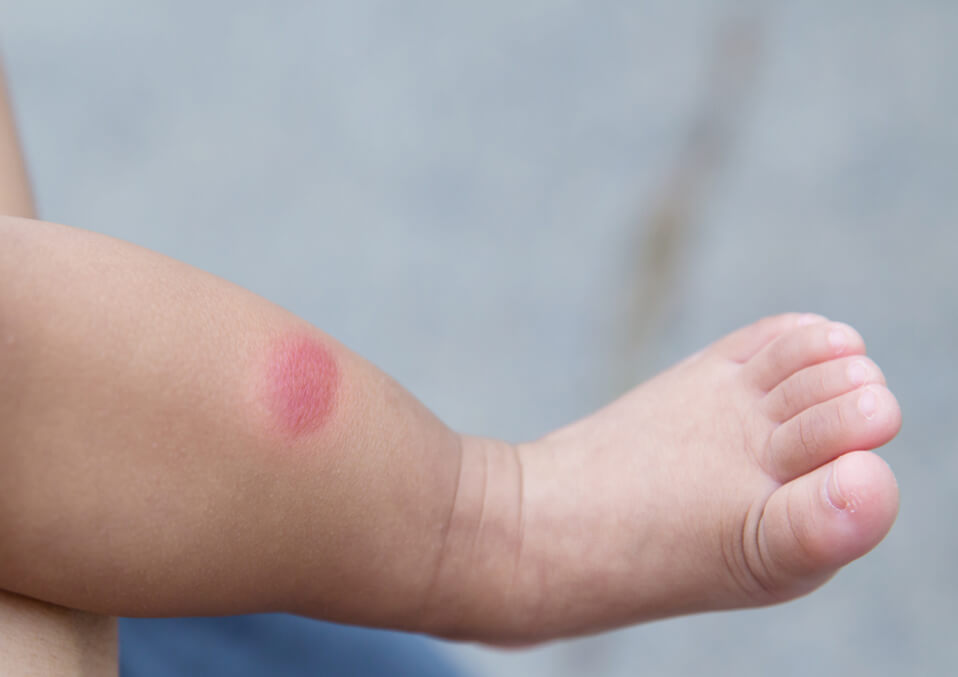
It is just normal for babies to experience some side-effects when given a shot. These are just temporary and safe. Remember that these side effects just proves that the vaccine is working and that your child is making new antibodies.
- Tenderness and redness of the area.
- Slight swelling or rash in the area.
- Mild fever.
- Trouble sleeping.
These reactions will go away after a few days. Besides, these mild reactions are far more incomparable to the protection he will get against serious illnesses.
Help a kid relaxed during vaccination
Some parents are anxious about giving shots to their kids because it is painful and it may scare him. That is why it is better to follow the vaccination schedule so that the kid will not be overwhelmed with the number of shots he receives in a visit. There are diverting strategies that a parent or a doctor can use to make the baby remain calm. Parents can bring their child’s favorite toys or book when going to the clinic for a shot. It is necessary to keep him cool before and during the procedures. You can embrace your little one while singing his favorite nursery song. You can also talk to him using a soft, soothing tone. Maintaining eye contact is an essence so he will not divert his attention to the needle. You can even breastfeed a baby during vaccination since skin contact swelling and the sweet taste of a mother’s milk naturally relieves pain. Babies can sense anxiety and fear, so parents should be the first to keep calm during a session.
Risks of not getting vaccinated
Professional says that it takes a week for a vaccine to take effect and protect one who receives it. It is advised to have your kids get vaccinated before he is exposed to different risks, like when traveling or a disease outbreak.
Read also: The best quick meals snacks and treats for kids
If a kid is not vaccinated, he is prone to catch the disease from anyone and everywhere, putting him in numerous health hazards. Inform your child’s school and childcare facility about your child’s vaccination status so that they will know the proper approach to treating your child just in case. Isolate your child during outbreaks, especially in infants who are too young to be vaccinated. Be prepared that there are times when your kids can be asked to stay away from the school and other organized activities, especially if there are threats. It will not only make your child safe but the other kids as well. In case of traveling abroad, check first on a country’s Center for Disease Control if there will be any risk for a child who is not vaccinated.
So it is better to talk to your pediatricians to prepare a vaccination schedule to protect not only your kids but other kids whom he interacts with.
Read also:
- How Serious is Whooping Coughs for Babies
- Baby Health: Mandatory Medical Examinations
- Useful Health Tips for Your babies to Grow Healthy and Smart


